Notion is a great tool for note-taking and managing your projects. After the introduction of Notion API, it becomes very easy for developers to make custom integration. Custom integration solves specific issues and makes a streamlined workflow.
In this blog, you will see how to make Notion integration and read databases and page content.
Create Notion Integration
To create a new Notion integration, first, go to https://www.notion.so/my-integrations and click on the New Integration button.
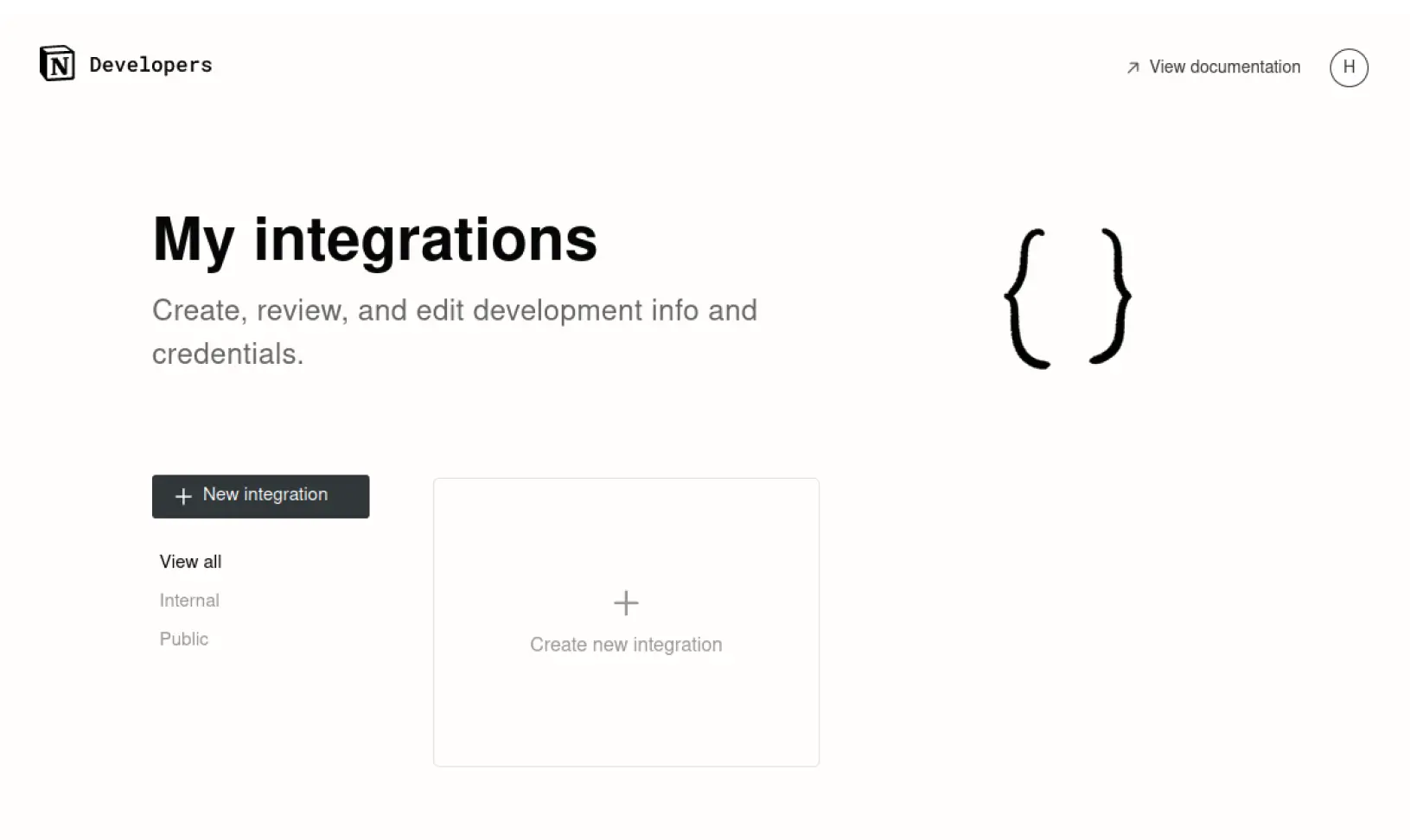
Then Add your basic information and submit it to get the API key. You will need this API key later in this tutorial to query Notion databases.
Add Connection to the Database
Now open your database as full-page in your browser and copy the URL. Paste the URL in a notepad to extract the database ID from there.
https://www.notion.so/fer6ff3d5fcs3dff1d2134349192cc?v=4rf43545...
|---------Database ID----------|
The random string between / and ?v is your database ID.
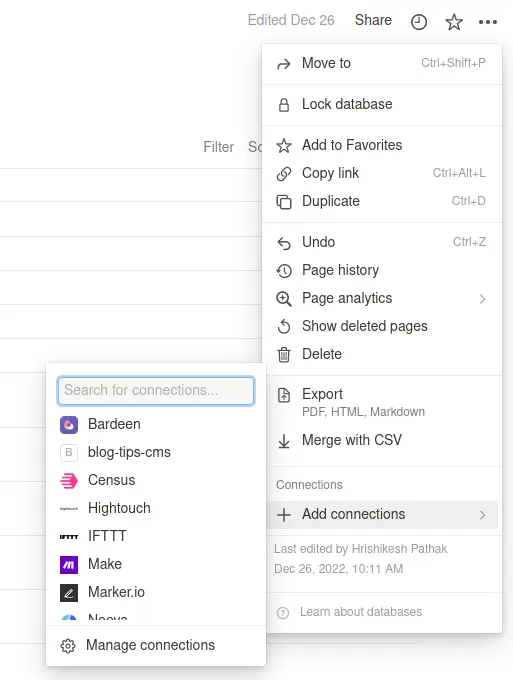
Now click on the three-dot icon on the database page and add your newly created connection by searching on the connection popup.
Creating a NodeJS project
To create a NodeJS project, run npm init -y in an empty directory. We use @notionhq/client to communicate with Notion. To secure the Notion API key and database ID, we use environment variables. Therefore dotenv package is required. Let’s install all the required dependencies.
npm i @notionhq/client dotenv
Now create a .env file in the project directory and paste your Notion API key and the database ID.
NOTION_DATABASE_ID="notion database id"
NOTION_KEY="notion API key"
Query a database
First, create an index.js file and import @notionhq/client.
require("dotenv").config();
const { Client } = require("@notionhq/client");
const notion = new Client({ auth: process.env.NOTION_KEY });
const databaseId = process.env.NOTION_DATABASE_ID;
Then initiate the Client object with the notion API key. Store the database ID in databaseId variable.
Query a Notion Database and retrieve its properties
To query a notion database use notion.databases.query() method and add the database_id parameter. Then await the response and log the value to see the response.
async function retriveDb() {
const response = await notion.databases.query({
database_id: databaseId,
});
console.log(response);
}
The demo response should look like this.
{
object: 'list',
results: [
{
object: 'page',
id: '88923jke3e-38aa-4841-aa0b-a29134reff65',
created_time: '2023-04-27T10:37:00.000Z',
last_edited_time: '2023-04-28T06:31:00.000Z',
created_by: [Object],
last_edited_by: [Object],
cover: null,
icon: null,
parent: [Object],
archived: false,
properties: [Object],
url: 'https://www.notion.so/Read-Notion-databases-using-Notion-API'
},
{
object: 'page',
id: '3lknd475-385b-4bd1-dfnl-4a5sdsdsd621d',
created_time: '2023-04-23T16:56:00.000Z',
last_edited_time: '2023-04-27T06:50:00.000Z',
created_by: [Object],
last_edited_by: [Object],
cover: null,
icon: null,
parent: [Object],
archived: false,
properties: [Object],
url: 'https://www.notion.so/How-to-add-a-Newsletter-to-your-website-for-free'
},
],
next_cursor: null,
has_more: false,
type: 'page',
page: {}
}
The response lists all the items in the database with their properties. You can use their id to read the respective pages. To see the properties of each item, tweak the console.log command a bit.
console.log(response.results.map((item) => item));
The new log should look like this.
[
{
status: { id: 'DGz%40', type: 'status', status: [Object] },
slug: { id: 'STrk', type: 'rich_text', rich_text: [Array] },
description: { id: 'TMLN', type: 'rich_text', rich_text: [] },
tags: { id: 'dnzg', type: 'multi_select', multi_select: [Array] },
Name: { id: 'title', type: 'title', title: [Array] }
},
{
status: { id: 'DGz%40', type: 'status', status: [Object] },
slug: { id: 'STrk', type: 'rich_text', rich_text: [Array] },
description: { id: 'TMLN', type: 'rich_text', rich_text: [Array] },
tags: { id: 'dnzg', type: 'multi_select', multi_select: [Array] },
Name: { id: 'title', type: 'title', title: [Array] }
},
]
Here, status, slug, description, tags, and Name are the properties of the database.
Retrieve pages
Copy the id of the pages from the above response and call the notion.block.children.list() method to list all the items inside a page.
async function retrivePageContent() {
const blockID = "88923jke3e-38aa-4841-aa0b-a29134reff65";
const response = await notion.blocks.children.list({ block_id: blockID });
console.log(response);
}
The demo response of this method looks like this.
{
object: 'list',
results: [
{
object: 'block',
id: '3a8418ac-rt8c-4d4a-8cc0-ecsdfsdferd4deb',
parent: [Object],
created_time: '2023-04-17T18:29:00.000Z',
last_edited_time: '2023-04-17T18:30:00.000Z',
created_by: [Object],
last_edited_by: [Object],
has_children: false,
archived: false,
type: 'paragraph',
paragraph: [Object]
},
{
object: 'block',
id: '63dfgf429-a2a2-45d5-dkmnf-8c75325fgdea',
parent: [Object],
created_time: '2023-04-17T18:22:00.000Z',
last_edited_time: '2023-04-17T18:31:00.000Z',
created_by: [Object],
last_edited_by: [Object],
has_children: false,
archived: false,
type: 'heading_2',
heading_2: [Object]
},
],
next_cursor: null,
has_more: false,
type: 'block',
block: {}
}
Here you can see, the response contain paragraph and headings of the page. The response contains user-defined blocks. A block may be a paragraph, heading, images, etc.
If you want to retrieve the plain texts of each block, then change the console.log command a little bit.
console.log(response.results.map((block) => block[block.type].rich_text));
Conclusion
Reading a notion database is very easy. Now you have learned how to make notion integration, how to query a database, and at last retrieve page content using notion API. You can use this knowledge to make something useful for your own.
If you have any queries, please drop me a mail, and don’t forget to subscribe to my newsletter.
